The impact of quantum principles on devices
Quantum principles, once confined to theoretical physics, are increasingly influencing the design and functionality of modern devices across various sectors. This fundamental shift in understanding how matter and energy behave at the atomic and subatomic levels is paving the way for advancements that could redefine the capabilities of technology, from how information is processed and stored to the precision of sensors and the security of digital communications. Exploring this impact reveals a future where devices operate with unprecedented efficiency and power.
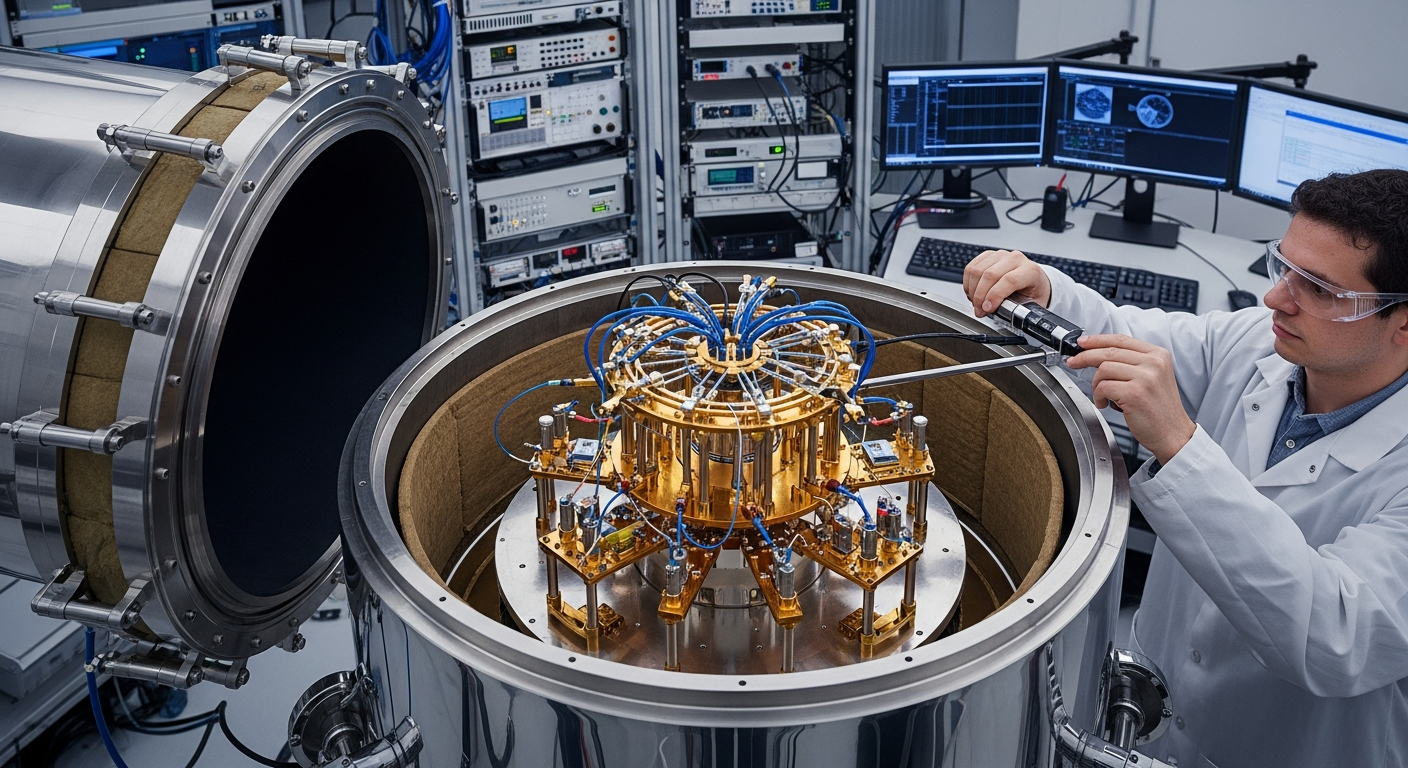
Quantum Effects in Modern Device Hardware
The inherent properties of quantum mechanics already play a crucial role in the functionality of many contemporary electronic devices, even if they aren’t explicitly quantum computers. Transistors, the foundational building blocks of all modern “hardware” and integrated “chip” “design”, rely on quantum tunneling and band theory to control electron flow. As manufacturers continue to shrink the size of these “components” to enhance performance, quantum effects become more pronounced. Understanding and manipulating these phenomena are essential for pushing the boundaries of miniaturization and improving the efficiency of conventional “digital” “circuit”ry.
Advancements in Computing and Data Processing
The most prominent and often discussed impact of quantum principles is on “computing”. Quantum computers leverage phenomena like superposition and entanglement to perform calculations that are intractable for classical machines. This paradigm shift in “processing” power holds immense potential for complex problem-solving, such as drug discovery, materials science, and financial modeling. Beyond raw computational speed, quantum principles could revolutionize “data” “storage” by enabling denser and more secure memory solutions, forming the basis of entirely new “system” architectures and driving significant “innovation” in the field.
Enhancing Sensor Technology and Digital Interfaces
Quantum mechanics offers pathways to create highly sensitive and accurate “sensor” “technology”. Devices utilizing quantum principles can detect minute changes in magnetic fields, gravity, and temperature with unparalleled precision. This leads to advancements in navigation “devices”, medical imaging, and environmental monitoring. Furthermore, the development of quantum-enhanced displays could offer improved resolution, color accuracy, and energy efficiency, transforming the visual “interface” through which users interact with “digital” content. These quantum-inspired sensors and display “components” promise to make devices more intelligent and responsive to their environment.
Implications for Network and Power Systems
The principles of quantum mechanics also extend their influence to communication “network”s and “power” management. Quantum cryptography, for instance, offers theoretically unbreakable encryption methods, providing a new layer of security for “data” transmission over “network”s. This is vital in an increasingly interconnected world where data privacy and integrity are paramount. In terms of “power”, research into quantum materials could lead to more efficient energy generation, transmission, and storage solutions, potentially reducing energy consumption in devices and contributing to more sustainable “automation” and operation of complex systems.
Future Prospects and Design Challenges
The integration of quantum principles into mainstream “technology” presents both exciting prospects and significant “design” challenges. While quantum computing is still in its nascent stages, its eventual maturation could lead to breakthroughs in artificial intelligence, optimization, and scientific discovery. However, developing stable qubits, managing quantum coherence, and engineering scalable quantum architectures require substantial research and development. The future of “device” “innovation” will likely involve a hybrid approach, where quantum accelerators augment classical processors, pushing the boundaries of what is currently possible in various applications.
The transformative potential of quantum principles on devices is profound, promising to reshape the landscape of technology. From enhancing the fundamental “hardware” of existing electronics to enabling entirely new forms of “computing” and “data” “processing”, quantum mechanics is driving a wave of “innovation”. As research progresses, we can anticipate more sensitive “sensor”s, more secure “network”s, and more efficient “power” “system”s, leading to a new generation of sophisticated and capable “digital” “device”s designed with quantum insights at their core.





